Dwarf Planets of Our Solar System
In 2006, the organization responsible for classifying celestial bodies, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) decided that a new class of objects was needed. Pluto, considered a planet since its discovery in 1930, was reclassified into the new “dwarf planet” category. To date, five dwarf planets have been found, although some astronomers expect there may be as many as 50 in the solar system.
 Source: space
Source: space
How to Observe the Moon
The earth’s satellite is a spectacular sight even with the naked eye. With a small telescope or pair of binoculars, the view is even more amazing. Dark, flat plains called Maria, deep craters and bright rays of ejected material pepper the rugged surface.
 Source: space
Source: space
Curiosity 7 Minutes of Terror
To ensure a successful entry, descent, and landing, engineers begin intensive preparations during the approach phase, 45 days before the spacecraft enters the Martian atmosphere.
 Source: nasa
Source: nasa
Meteors
Meteors can appear both day and night, but the daytime ones are harder to see unless they are exceptionally bright. The “meteor” itself is the trail of incandescent air caused by a piece of space debris streaking through the atmosphere.
 Source: space
Source: space
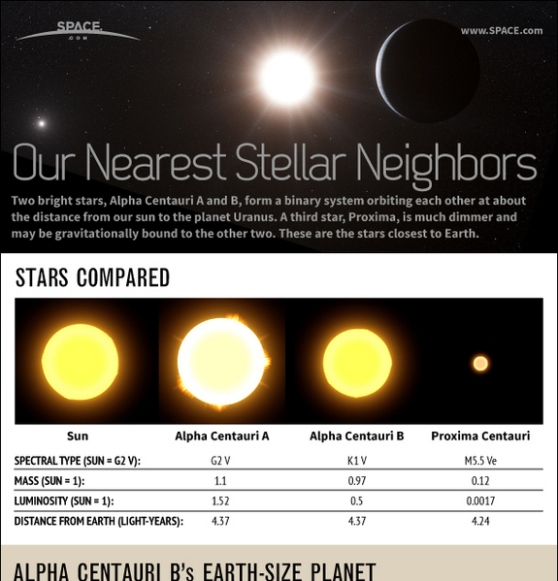
Alpha Centauri Stars & Planet Explained: Our Nearest Neighbors
Two bright stars, Alpha Centauri A and B, form a binary system orbiting each other at about the distance from our sun to the planet Uranus. A third star, Proxima, is much dimmer and may be gravitationally bound to the other two. These are the stars closest to Earth.
 Source: space
Source: space
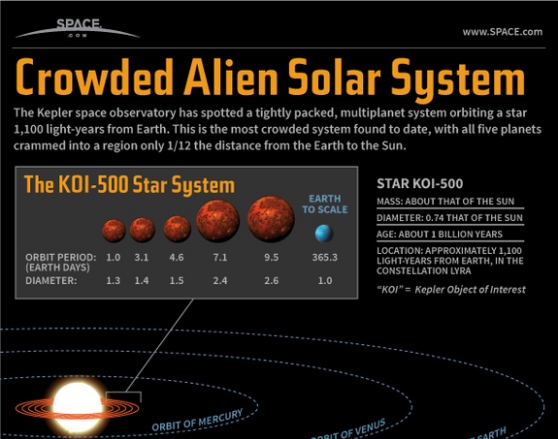
Tiny Alien Solar System Discovery Explained
The Kepler Space observatory has spotted a tightly packed, multiplanet system orbiting a star 1,100 light-years from earth. This is the most crowded system found to date, with all five planets crammed into a region only 1/12 the distance from the Earth to the Sun.
 Source: space
Source: space
Space Jump: How Daredevil’s Record-Breaking Supersonic Skydive Works
From a capsule suspended 23 miles (36.6 kilometers) above Roswell, N.M., daredevil Felix Baumgartner dives in an attempt to set a new altitude record.
 Source: space
Source: space
How Virgin Galactic’s Space Ship Two Passengers Space Plane Works
Virgin’s second-generation space plane is the sequel to its award-winning Spaceship One. The new craft is launched from an airplane, fires a rocket to again altitude, then re-enters the atmosphere and glides to a landing.
 Source: space
Source: space
How SpaceX’s Dragon Space Capsule Works
Developed for NASA to service the International Space Station, the reusable Dragon capsule is lofted into orbit by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. While the first flights are to carry cargo only, the capsule was designed to be capable of carrying up to seven astronauts.
 Source: space
Source: space
Sputnik: How the World’s 1st Artificial Satellite Worked
By the 1950s, scientists all over the world realized that it was becoming practical to launch an object into a circular path around the Earth. In mid-1955, the United States announced that it would launch the first satellite to commemorate the International Geophysical Year in 1957. The Soviet Union realized that 1957 was the 40th anniversary of the Bolshevik Revolution.
 Source: space
Source: space
Mars Rover Curiosity’s Ancient Stream Discovery Explained
While rolling across the floor of Gale Crater on Mars, the rover Curiosity has found rock formations that scientists say reveal clear evidence of water flowing in past ages.
 Source: space
Source: space
Moscow’s Secret Moon Plan – The N-1 Rocket
Hoping to beat the Americans to the moon before 1970, Soviet rocket engineer Sergey Korolyov worked in secret to plan the mighty N-1, an equal to the American Saturn V booster. In 1966 however, the sudden death of Korolyov threw Soviet plans ionto disarray. After four N-1s were lost in catastrophic accidents, the Soviets destroyed the remaining hardware and denied the very existence of the program. The N-1 remained a state secret until being made public in 1990.
 Source: space
Source: space
How NASA’s Asteroid Sample Return Mission Will Work
Scheduled for launch in 2016, The OSIRIS-Rex probe should intercept asteroid RQ36 in 2020. This asteroid is believed to contain pristine samples of the earliest materials that formed our solar system 4.5 billion years ago. RQ36 also poses a threat to humanity: it has a possibility of colliding with Earth roughly 170 years from now.
 Source: space
Source: space
1st American in Orbit: How NASA & John Glenn made History
On Feb.20, 1962, 40-year-old Marine pilot John Glenn became the third American to be launched into space as well as the third human to orbit the earth. Glenn’s tiny Mercury capsule completed three circuits of the globe.
 Source: space
Source: space
How Interstellar Space Travel Works
Even the fastest humans and spacecraft launched thus far would take many thousands of years to reach the closest stars. Speeds about 75 times faster than this would be required if we hope to make an interstellar trip in less than a hundred years.
 Source: space
Source: space
Venus Transit of the Sun: A 2012 Observer’s Guide
When the orbital positions are just right, the two planets whose orbits are smaller than Earth’s – Mercury and Venus – cross the sun’s disc as seen from our vantage point. These events are called transits. Due to the fact that the orbits are tilted with respect to each other, a transit is a rare event.
 Source: space
Source: space
Inside Russia’s Mars Moon Sampling Mission
“Grunt” means “ground” or “soil” in Russian. The robotic probe, which is estimated to cost $ 163 million, was launched on a Zenit-2SB rocket with the goal of collecting a sample from Mars’ moon Phobos and returning it to earth. The probe weighs 29,775 Ibs (13,505 kg) of which 110 Ibs (50kg) is scientific equipment.
 Source: space
Source: space
Spaceships of the World: 50 Years of Human Spaceflight
Beginning with Russian pilot Yuri Gagarin in 1961, more than 500 people have been launched into space in a variety of vessels. Twelve people have walked on the moon, and an additional 14 have flown over the moon without landing.
 Source: space
Source: space
How Japan’s Hayabusa Asteroid Mission Worked
The Japanese probe Hayabusa has overcome systems failures and misfortunes to become the first-ever probe to sample an asteroid and return home to Earth.
 Source: space
Source: space
The International Space Station: Inside and Out
Begun in 1998 with the launch of the first component from Russia, the construction of the International Space Station (ISS) is the most complex space project ever undertaken. At $100 billion it is in fact the single most expensive object ever built.
 Source: space
Source: space

